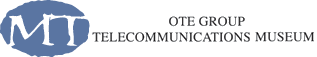VoIP – The convergence of telephony and information technology
In recent years, we have often heard about VoIP technology in telecommunications. However, this technology is the result of technological developments that date back several decades.
But what is VoIP?
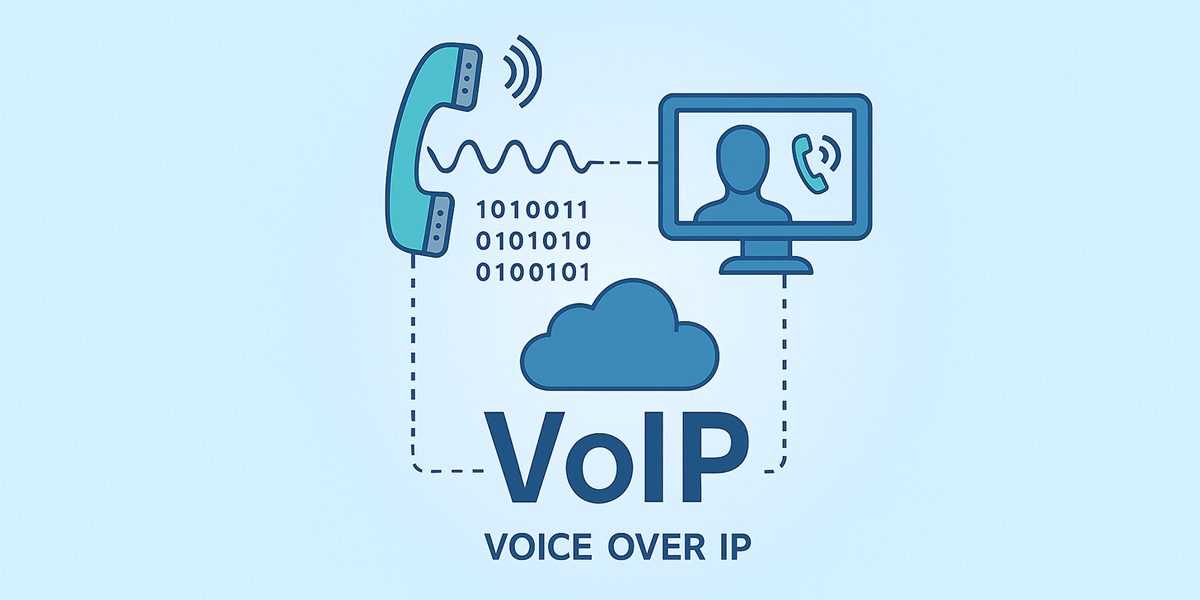
VoIP (Voice over IP) is a technology that allows voice to be converted into digital data and sent over the Internet instead of traditional telephone lines. This enables the integration of VoIP technology into various digital devices — such as IP phones, tablets, laptops, and smart TVs—through a shared IP-based network, where voice and data converge seamlessly through a router and a broadband Internet connection.
What preceded it technologically?
Information technology and telecommunications do not share a common origin. Telecommunications began in the 19th century with the telegraph and the telephone using analog signals and circuit switching, i.e., transmission between two points with a continuous connection between them throughout the duration of the communication. Information technology, on the other hand, as it developed after World War II and in connection with the introduction of network technologies, is based on packet switching communication technology, i.e., communication where the data of the transmitted information is divided into small pieces, or "packets," and sent independently through a network to their destination.
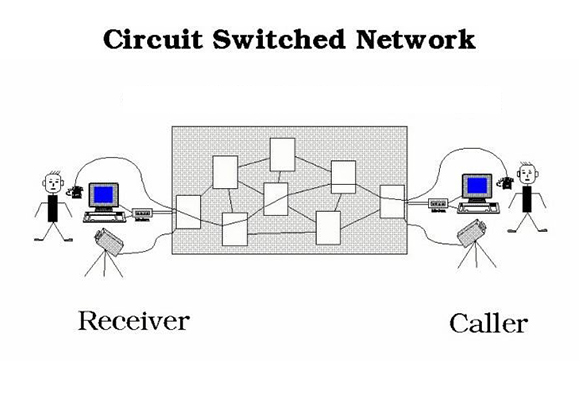
How was convergence achieved?
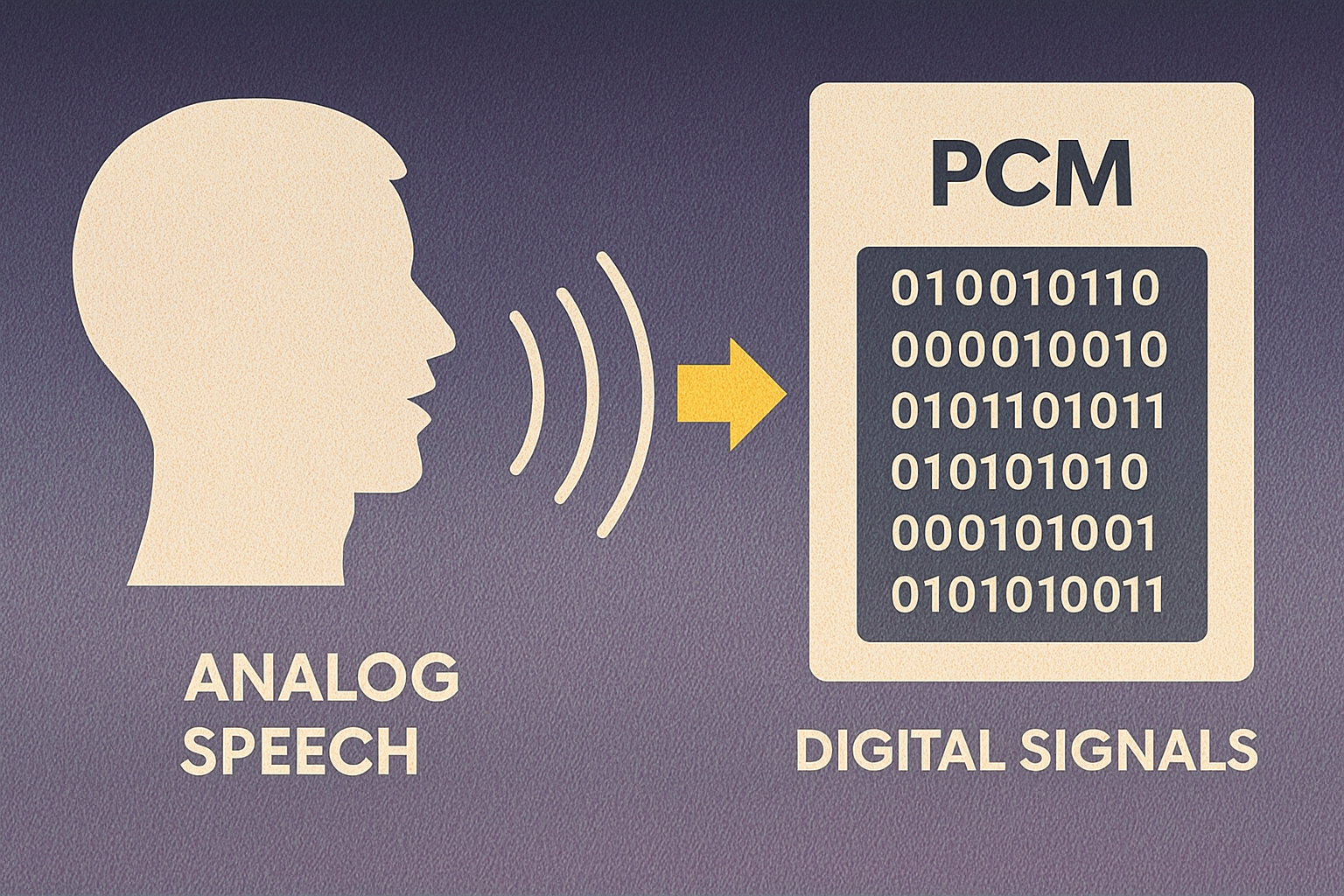
The convergence of information technology and telecommunications was made possible by several scientific and technological discoveries. In 1948, Claude Shannon's Information Theory established a common framework, showing that data, voice, and signals could be represented as information. During the 1960s and 1970s, the development of packet switching demonstrated that all types of information (whether text, images, or voice) could be transmitted in small digital packets rather than relying on dedicated circuits. At the same time, the digitization of voice through pulse code modulation (PCM) made it possible to convert analog speech into digital signals, laying the foundation for treating voice as data. Finally, advances in fiber optics and satellite communications in the 1970s and 1980s expanded network capacity, making large-scale digital traffic transmission feasible and efficient.
Where did this convergence process lead?
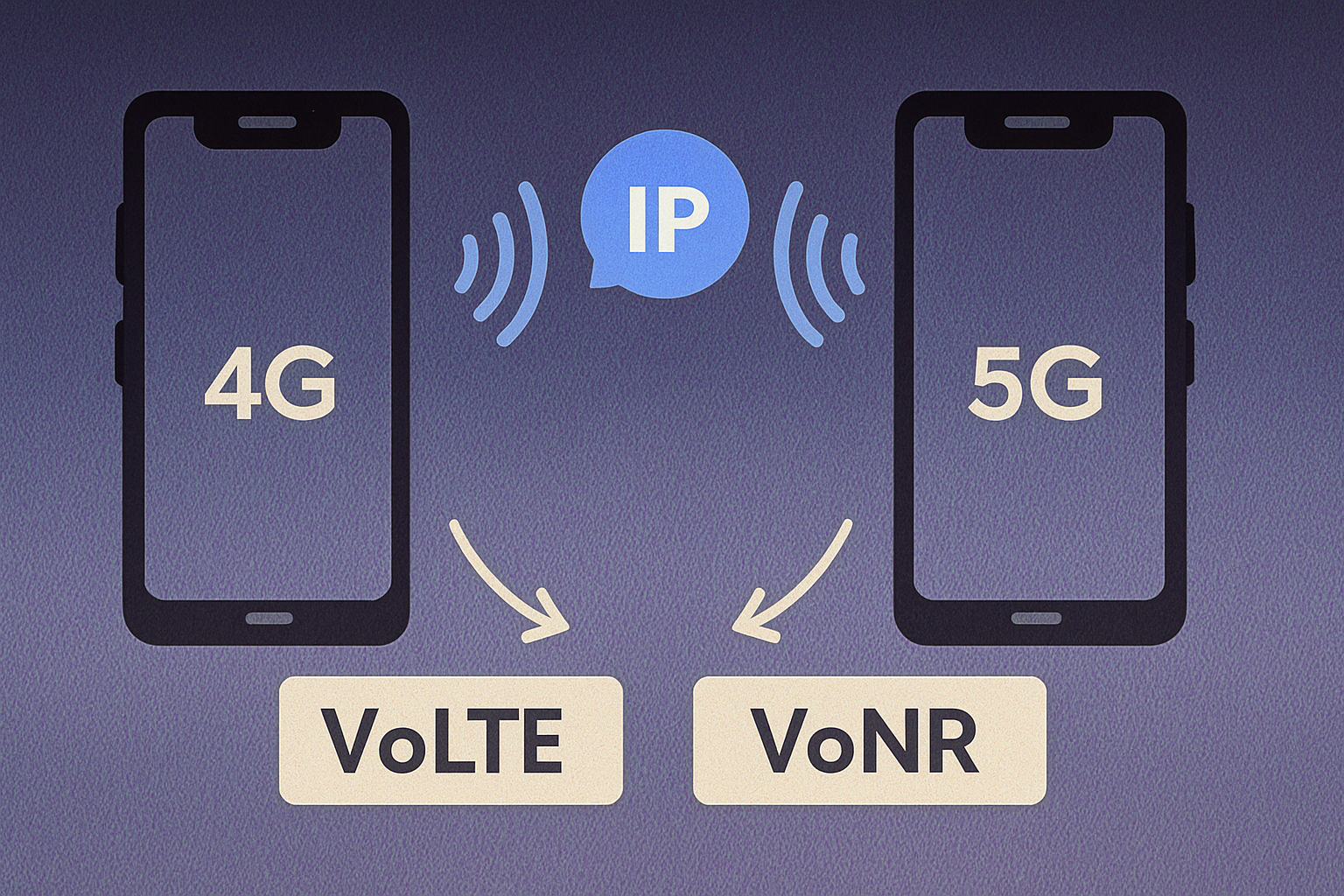
The ongoing digitization of telecommunications and the creation of Internet protocols, together with the growth of broadband, will enable VoIP to emerge as a pillar of modern telecommunications. Today, most telephone networks, including 4G/5G mobile networks, rely on IP technologies for voice transmission. Voice is transmitted using protocols such as VoLTE (Voice over LTE) or VoNR (Voice over NR), which apply VoIP principles to mobile phone networks.
Photographs:
- Illustration representing VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technology — converting voice signals into digital data for transmission over the internet, enabling phone and video calls through cloud-based communication systems.
- Diagram illustrating a VoIP home network setup, showing how a router and phone adapter connect various devices — such as an IP phone, smart TV, laptop, and tablet — through a DSL or cable modem to the internet. The setup demonstrates how voice and data services share the same broadband connection.
- Diagram showing a packet-switched network, where data from the caller is divided into small packets that travel independently across a network of interconnected nodes before being reassembled by the receiver. This method underlies modern internet communication and technologies such as VoIP and data transfer over IP networks.
- Illustration showing the conversion of analog speech into digital signals using Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) — a process that samples and quantizes voice waves into binary code, enabling digital transmission and storage of audio in modern telecommunication systems.
- Illustration showing IP-based voice communication in mobile networks — VoLTE (Voice over LTE) for 4G and VoNR (Voice over New Radio) for 5G. Both technologies transmit voice calls as data over the internet protocol, enabling faster connections and higher call quality in modern cellular systems.