Telstar 1 (1962): Telecommunications satellites are now a reality

Wireless telecommunications
The successful transmission of radio waves by Marconi in 1897 marks the beginning of wireless telecommunications. Radio waves (later including infrared radiation and microwaves), which are electromagnetic waves, travel through the atmosphere carrying telecommunication information. In 1901, the first transatlantic communication takes place. Wireless telecommunications help overcome the technical difficulties faced by wired infrastructures.

Technical limitations
Wireless telecommunications, however, also encounter several technical difficulties. Without satellites, communication through radio waves is restricted by various fundamental physical factors. Radio waves can propagate in three ways: by line-of-sight propagation, skywave propagation, or groundwave propagation. In the case of line-of-sight, the wave cannot be transmitted over long distances due to Earth’s curvature. The geometry of the Earth therefore limits transmission to relatively short straight-line paths. Skywaves, which are transmitted through reflection from the ionosphere, they are limited to the frequency range between 3 and 30 MHz, because otherwise, instead of being reflected, they penetrate the ionosphere and escape. Moreover, the usable frequency range depends on solar activity, the time of day, and the different layers of the ionosphere.
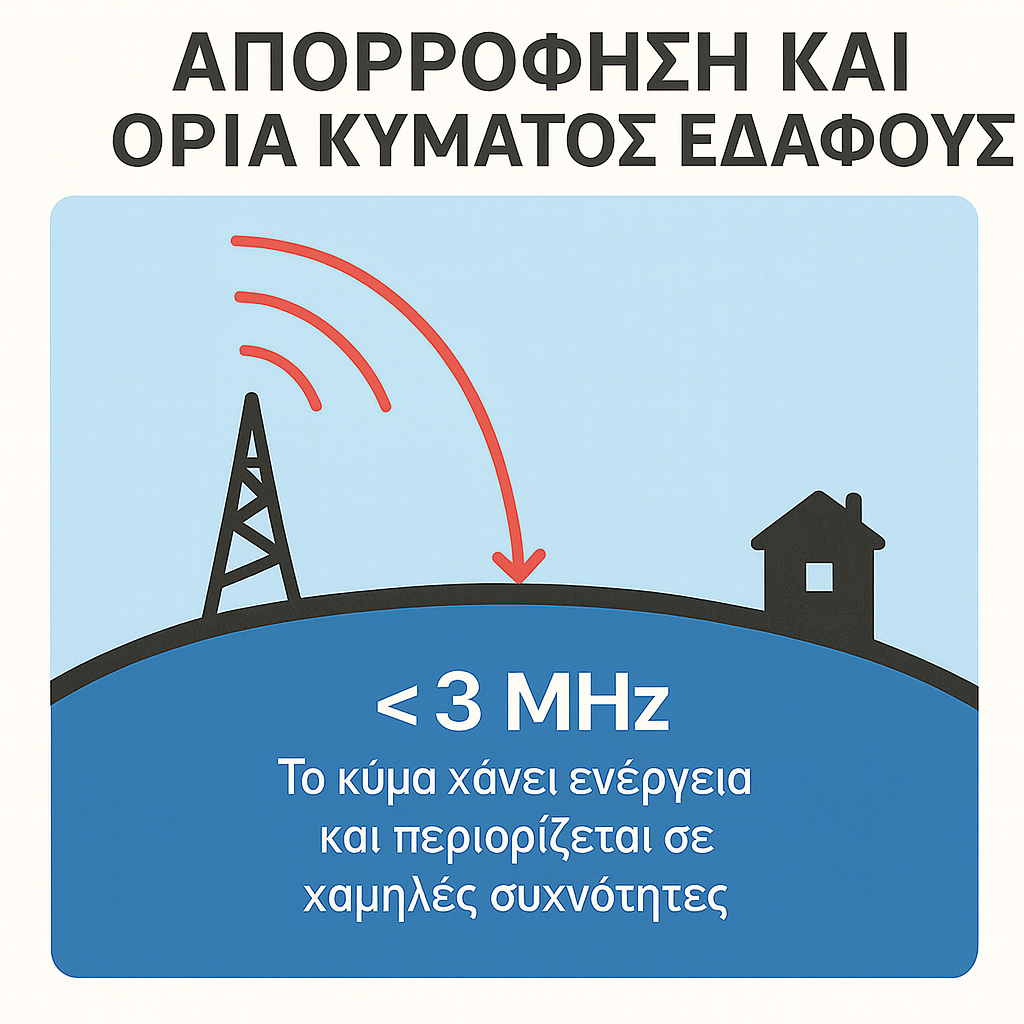
As for ground waves, although they follow the curvature of the Earth and travel close to the surface ‒allowing them to cover greater distances‒ gradually lose their energy, which is absorbed by the ground. They are also weakened by the presence of buildings, mountains, or any other obstacles. In practice, they cannot exceed frequencies of about 3 MHz. In practice, these limitations mean that radio-wave communication without satellites remains restricted to regional or local areas, requires extensive ground-based infrastructure, and cannot provide real-time global connectivity.

The breakthrough of satellites: the liberation of wireless telecommunications
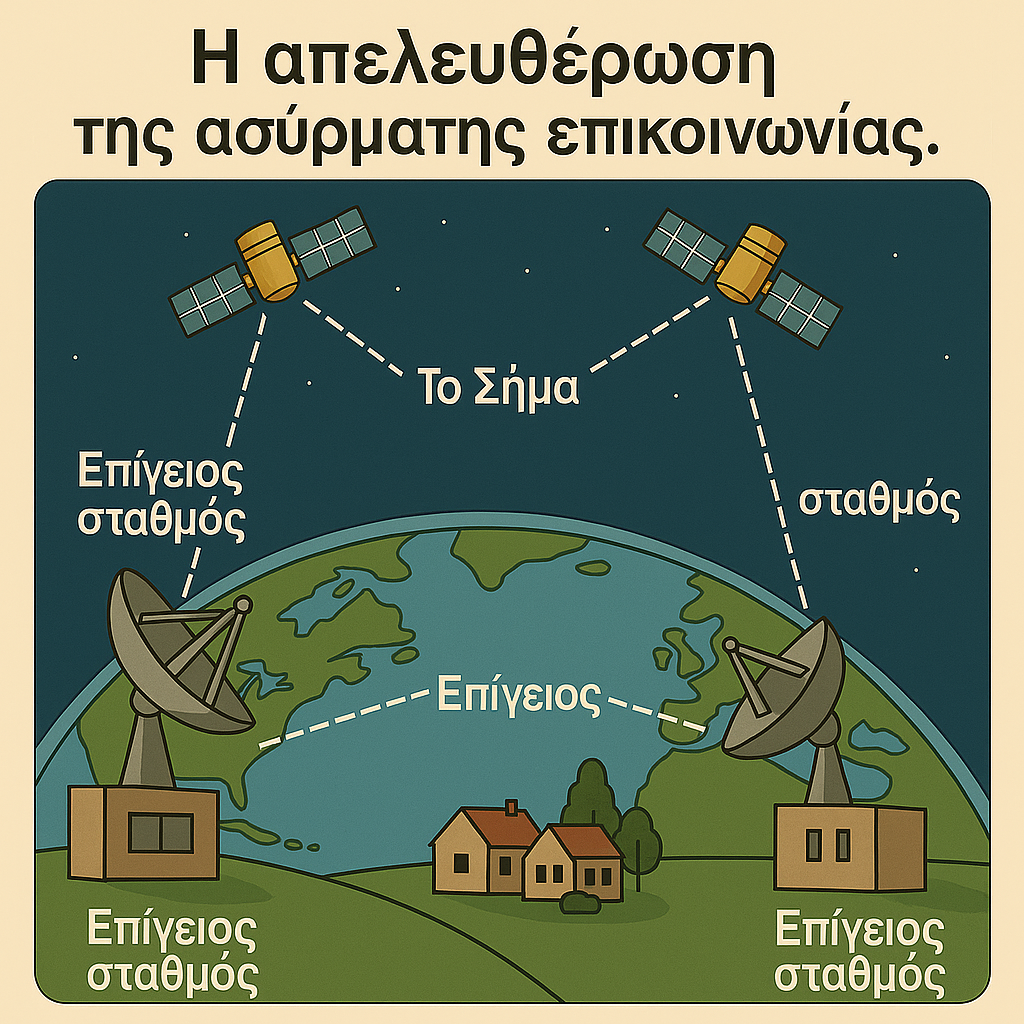
The system of satellite transmission enables uninterrupted communication even with regions that are extremely distant from the point of emission. The signal is sent from the Earth to a satellite and from there either to successive satellites and then to a ground station, or directly to a ground station. In this way, the physical limitations that previously hindered seamless signal transmission are overcome. Through satellites, communication with even the most remote areas of the planet ‒where equivalent terrestrial technical means are absent‒ becomes possible, dramatically expanding the geographical range of communication. These capabilities are not limited to telephony; they will also dramatically advance the transmission of television events on a global scale. Practically, they will greatly extend a long-running historical trajectory that continues today toward a world of human communication unified in both space and time.
Photographs:
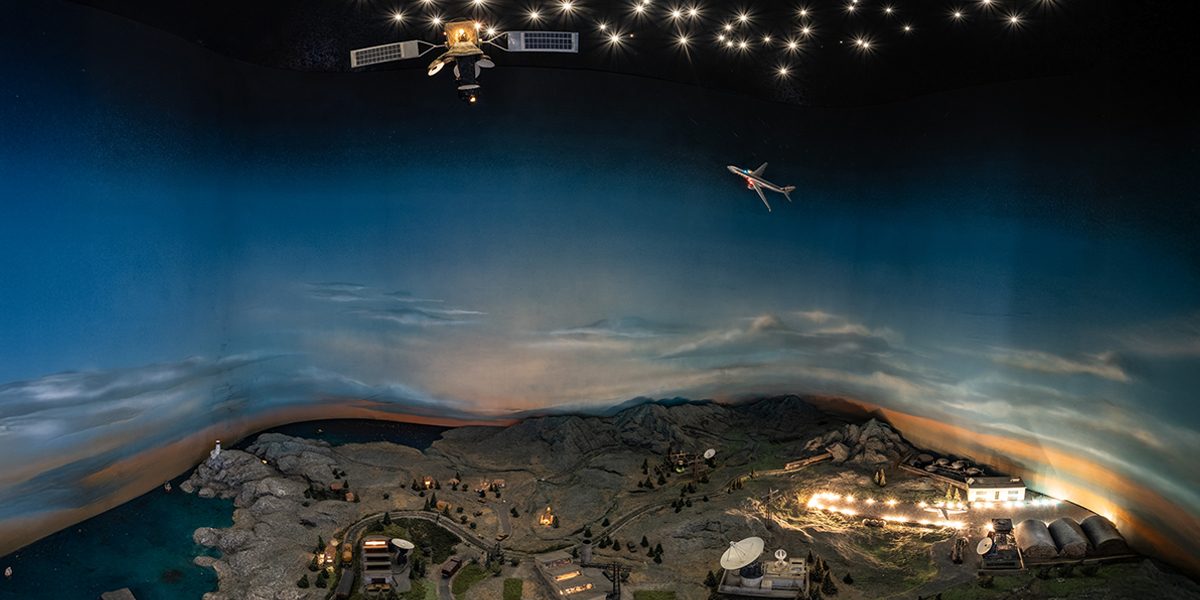
- Satellite center model (OTE Telecommunications Museum)
- Because the earth is curved, radio waves traveling straight cannot pass behind the horizon.
- Radio waves traveling close to the ground gradually lose energy and operate only at very low frequencies.
- Only frequencies of 3–30 MHz are reflected by the ionosphere; higher frequencies pass through it and are lost to space.
- Satellites carry the signal across the entire planet, allowing global wireless communication without physical barriers.